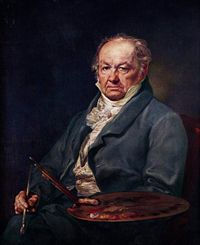(Fuendetodos, Saragossa, 1746 - Bordeaux, France 1828)
Francisco José de Goya y Lucientes, who was known as Francisco de Goya, was a Spanish painter and engraver. He was very influenced by Velazquez and Goya influenced a lot in the Contemporary painting.
His father was José Goya, who was from Saragossa and had Basque origins, was linked to the World of arts because of his job as gilder. Goya’s mother, Gracia Lucientes belonged to a farmworker family from Fuendetodos. The Goyas were spending some time at this town when Francisco was born. The town was very close to Saragossa, where Goya began to work in the studio of José Luzán. His earliest work belongs to this starting period, and it was a decoration in a wardrobe of the church of Fuendetodos. It was a painting realized with a lot of inexperience but it had a turbulent performance that presaged future freedoms.
Goya’s activity is almost unknown. It has been stated that between 1763 and 1766 he took part in two competitions in Madrid that were organized by the Academy of Fine Arts of San Fernando. Other painters were awarded and moreover, Goya received no votes from the academic board.
In April 1771 he was in Rome. Very few things are known from his stay in Italy. He paid the journey to Italy out of his own pocket and it had to be short in terms of time. When he was in Rome, he sent a canvas to a competition organized by the Academy of Parma, in which he was awarded with an honourable mention.
In the middle of 1771, Goya went back to Saragossa, where in October he was commissioned to paint the vault of the Basilica of the Pillar. He painted the frescoes known as Adoration of the Name of God, which was finished in the first half of 1772. It was a poor skilled composition but it has fragments of splendid quality.
In July 1773 he married Josefa Bayeu in Madrid. She was sister of the painters Francisco, Ramón and Manuel Bayeu.
Apart from some short duration journeys and until he immigrated to Bordeaux, Goya’s career was developed from that moment onwards in the capital.
Francisco Bayeu, who was from Saragossa, twelve years older than Goya and also was disciple of José Luzán, played a very important role in Goya’s life although there are no details about it. He could be Goya’s master and mentor because in 1771, when Goya participated in the competition of Parma, he stated that he was disciple of Bayeu. Thanks to Bayeu, already his brother-in-law, he began to work in the Royal Tapestry Factory. The 63 cartoons he realized between 1775 and 1792 are undoubtedly the juiciest compositions of that period. They demonstrate the progress in his technical skills, the sharpening of his palette and the ease of invention and observation that he later would develop through the following years.
The cartoons depicted subjects of popular and costumbrist nature, which were not chosen by Goya, but there, he had an opportunity to offer a fresh, kind and full of grace and humour point of view of the life surrounding him. In line with the skills he achieved with the cartoons and other similar paintings, he began to show himself to be a great portrait painter. Some of his portraits from the 1780s have a lively rococo style as we can see in Floridablanca, Duke and Duchess of Osuna, and The Marchioness of Pontejos; which are the first pieces within the incredible human gallery Goya would paint until his death.
The general development of the painting in Madrid during the 1770’s and the 1780’s was mainly influenced by the neoclassical sense derived from Mengs. Thanks to Goya’s pictorial discernment this crisis was overcome, and it was possible because he only reflected it with limitative results in some of his works, which were mainly those ones with religious subjects that were more typical to the dominant taste. Those artworks are Crucified Christ (1780), The Holy Family (El Prado Museum) and St. Bernardino of Siena.
Goya became an important painter at the Court before 1790. He was member of the Academy of San Fernando since 1780 and he attended regularly to the sessions. He enjoyed an economic welfare. He begins to establish himself as the portrait painter of the nobility. In 1786 he is appointed court painter.
During the winter of 1792-93 Goya fell very ill. The exact nature of his illness is unknown. It was according to Zapater “one of the most terrible ones” and it caused he went completely deaf. His deafness contributed in a powerful way to enrich the interior life of the artist and it promoted his imagination to areas that were unexplored till that moment.
He was hardly recovered from his illness, but he painted a group of canvases. The artworks The Madhouse, The Shipwreck and Fire belong to this period.
In 1975 he was made painting director of the Academy of San Fernando succeeding Francisco Bayeu. Two years later, he resigned from the post because of his deafness and undoubtedly it was also because of the total anti academic concept he had of the artistic education. He was appointed honorary director.
In 1799 his artistic career arrived to its peak after being appointed First Court Painter. His work as portrait painter was immense during that period and furthermore, his works were realized with an incredible pictorial wisdom and a sociological depth. He painted portraits of the king and the queen on foot and on horseback, and portraits of the entire royal family in his work The Family of Charles IV of Spain that combines a sublime quality with a documentary value, which reveals honestly the moral make-up of the personages. People in Court liked a lot this collective portrait, but it may be significant that Goya was not commissioned any portrait for the palace until 1808.
In 1808, when Ferdinand VII ascended the throne Goya portrayed him in his artwork Equestrian Portrait of Ferdinand VII of Spain (Academy of San Fernando). During October 1808, being at war with the French, Goya went to Saragossa after being called by Palafox to see and examine the ruins of the city. Josefa Bayeu died in 1812. The subsequent inventory of possessions shows that Goya had a well-off economic situation that was kept until his death.
During the following years, his style developed towards a greater expressive concentration. He renounced glazing in favour of a more direct and synthetic painting, his palette became simpler and curdled with matter, and he tended to sober colours and intonations and to a broad use of black colours.
In terms of religious painting, instead of outstanding the conventional Assumption and SS. Justa and Rufina; it is important to excel Prayer at Gethsemane and The Last Communion of St. Joseph of Calasanz, which may be his most deeply felt and authentic artworks of religious subject.
The liberals were persecuted in France, and it caused that Goya felt threatened. In May 1824, after the first repressive wave he asked king’s permission to go to a spa in Plombières, which was granted. At the end of June, he was in Bordeaux, which was the refuge for many Spanish liberal and supporters of the French during the Peninsular War. In April 16th 1828, he died in Bordeaux because of a paralysis when he was 82.